Formation of Castings
1. What is a Casting?
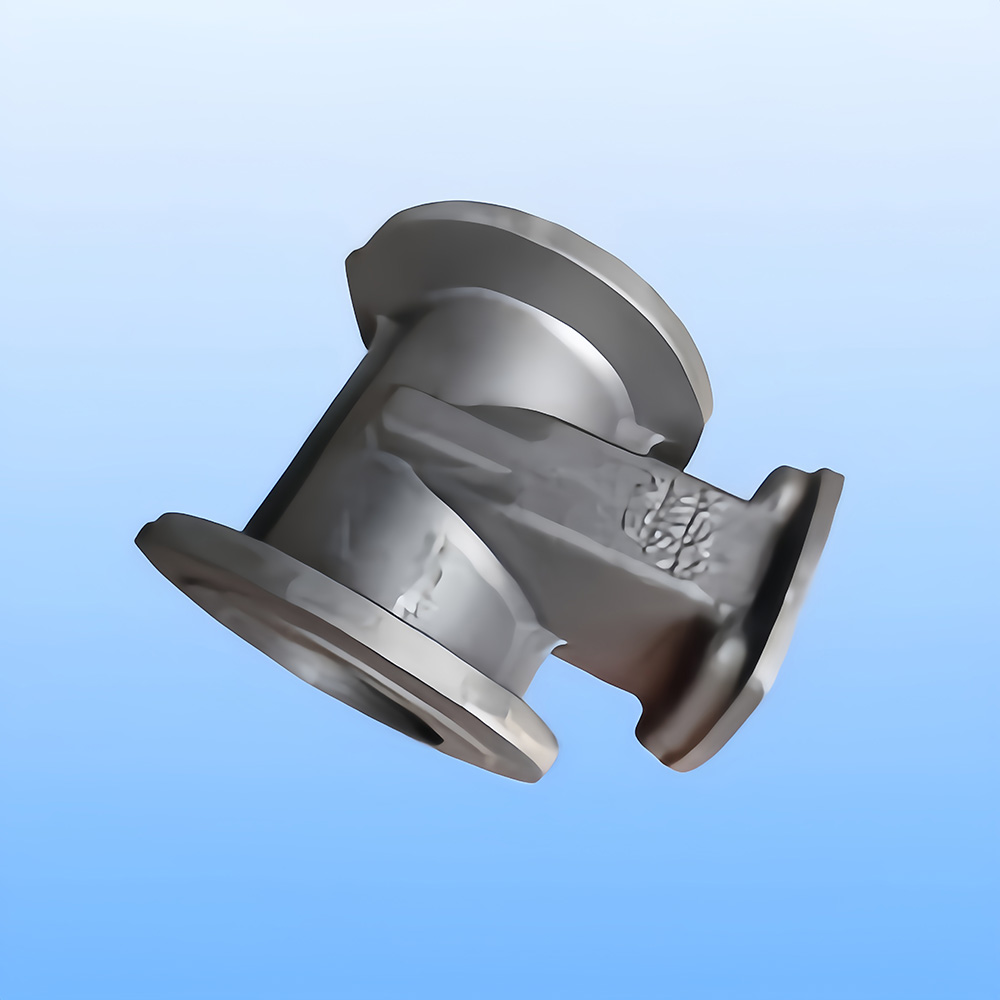
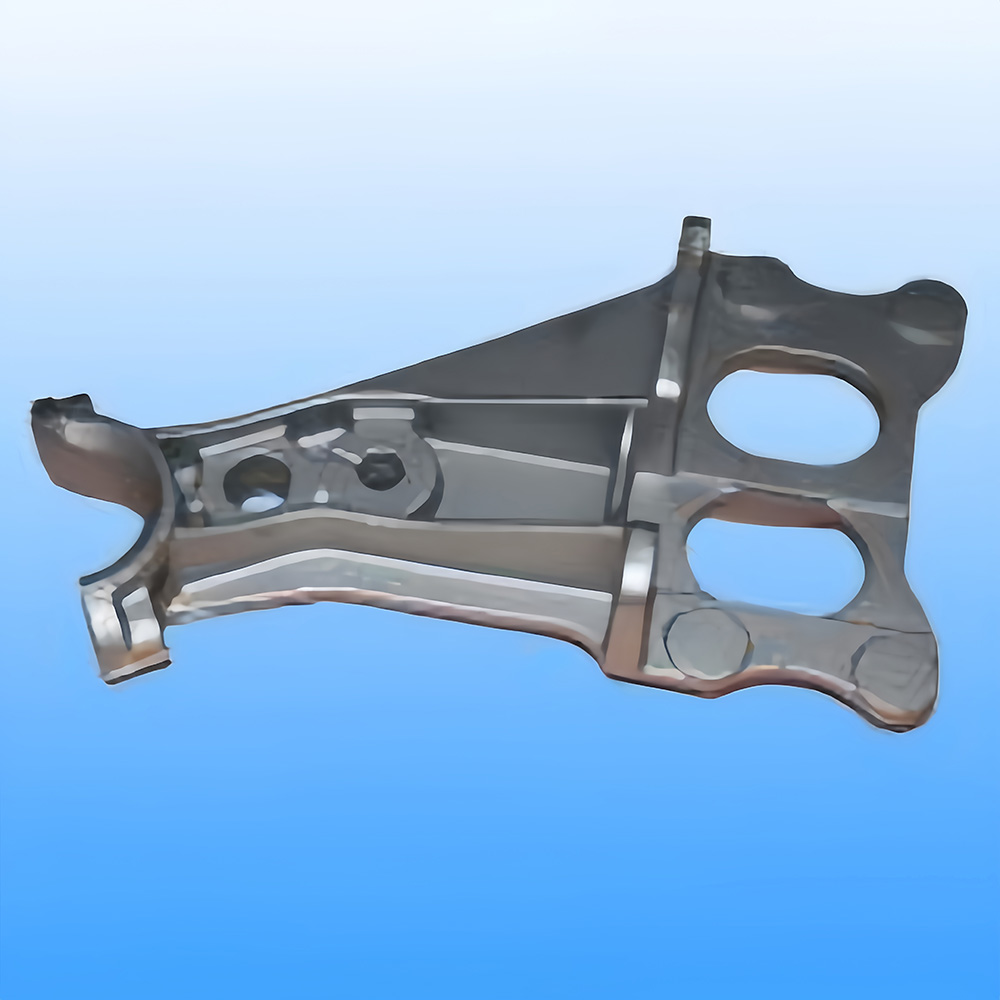
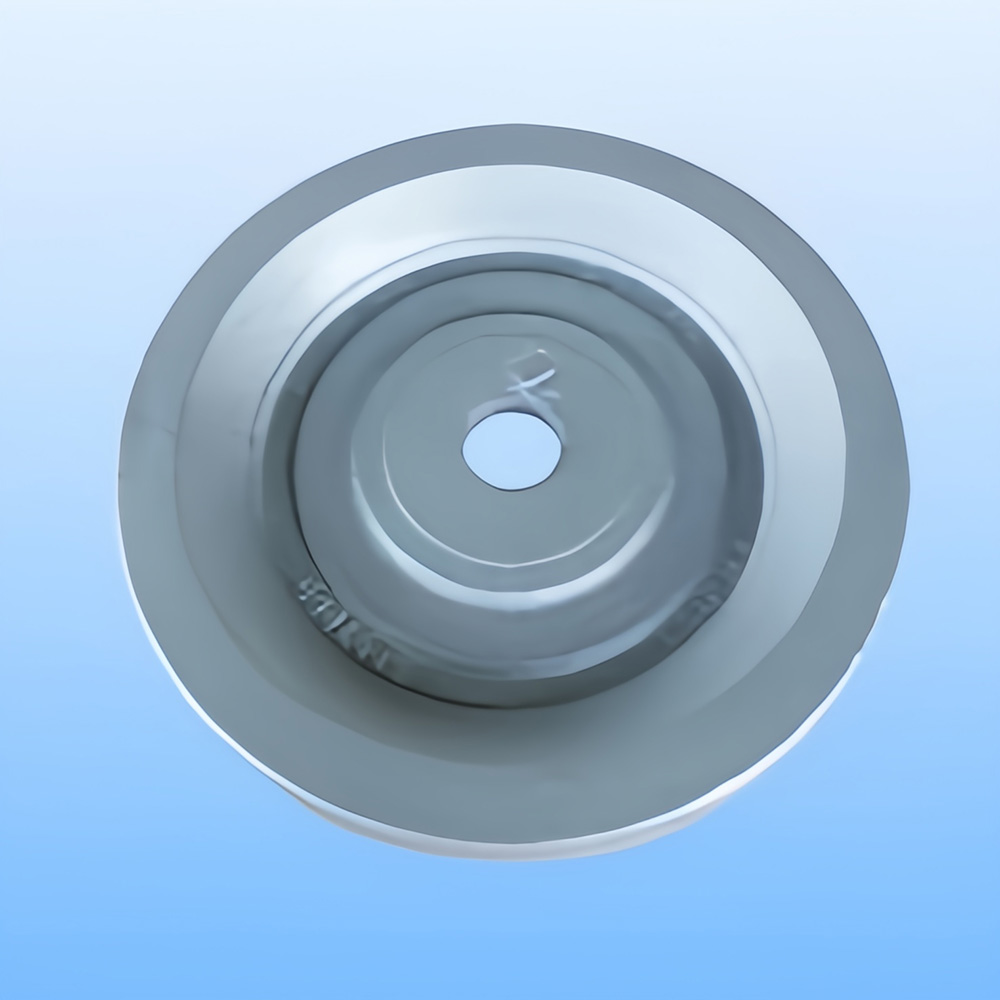
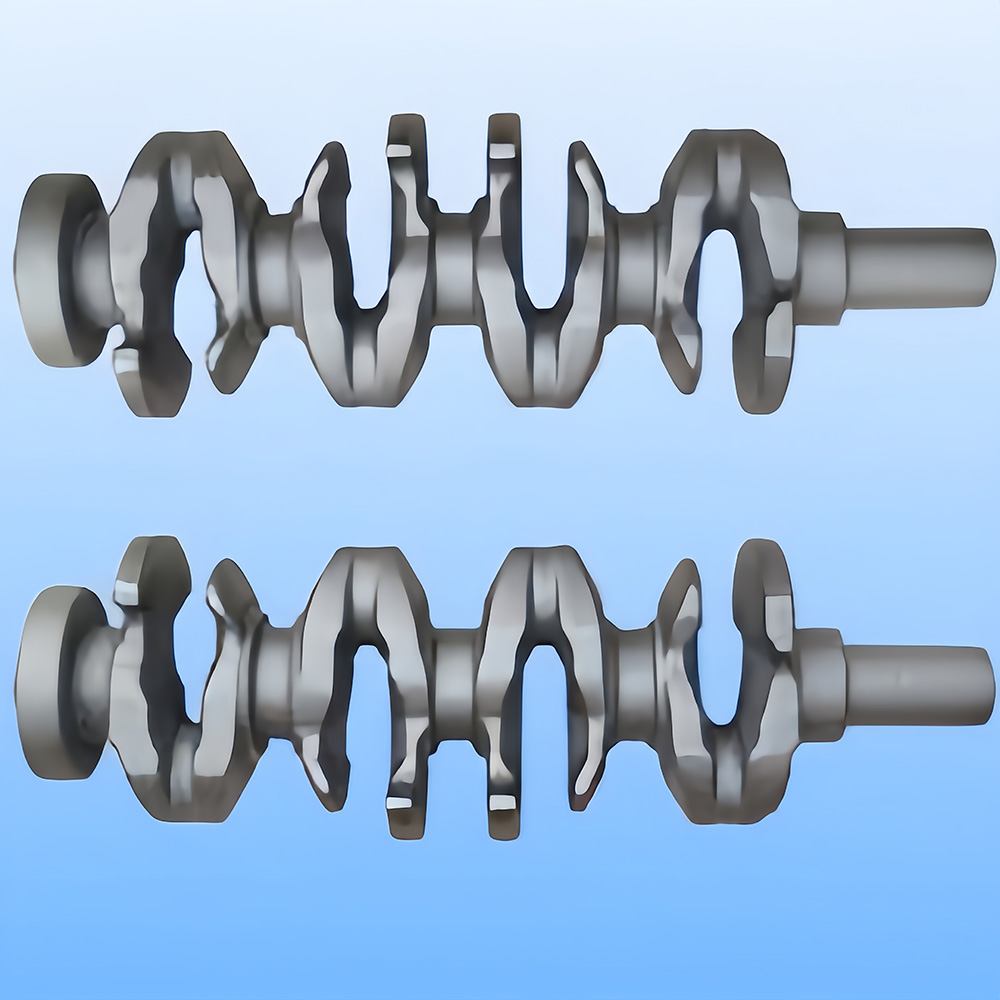
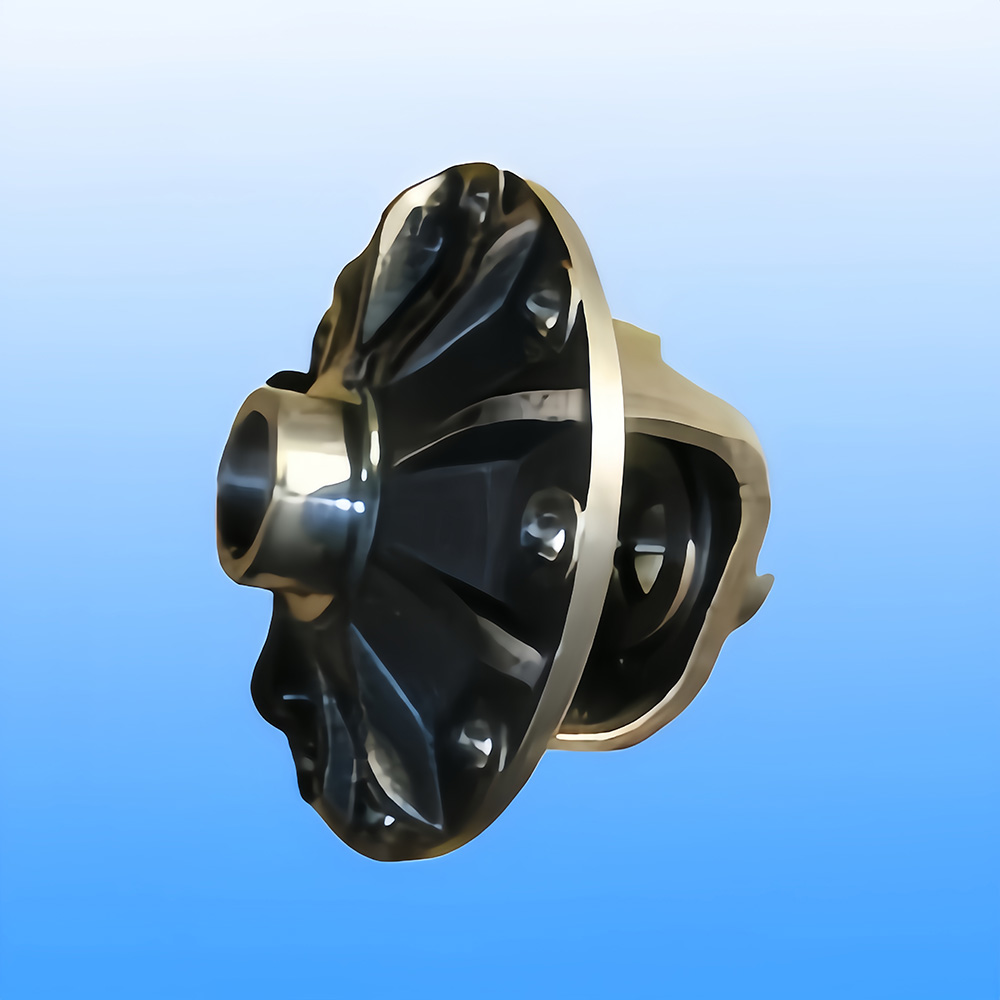
Definition: Casting is the method of pouring liquid metal into a mold cavity that matches the shape of the part, allowing it to cool and solidify to obtain the desired part or blank. The resulting product from this process is called a casting.
2. Advantages
**Capability to produce parts with complex shapes, especially those with intricate internal cavities (e.g., radiators).
**Wide adaptability, suitable for common industrial metal materials. Ranges from a few grams to hundreds of tons.
**Abundant raw material sources at low costs, including scrap steel, waste parts, and chips.
**The shape and size of castings are very close to the finished parts, reducing the amount of machining required, which falls under minimal or no cutting processing.
3. Disadvantages
**Mechanical properties are not as good as forgings (e.g., coarse grains, more defects).
**In sand casting, single-piece and small-batch production have high labor intensity.
**Casting quality is unstable, with many processes and complex influencing factors, making
4. Applications
Wide range of applications: Agricultural machinery 40~70% Machine tools: 70~80% weight castings
Next:no